Updated on September 16, 2025
Google Search Ads (specifically Search Ads and not Google PMax, Google Display, or Google Shopping Ads) let you connect with customers actively searching for your services. The ads, placed at the top or bottom of search results, ensure your business gets attention at the opportune moment, when potential customers are ready to sign up, book a call, or submit your contact form.
While Google Search Ads are ideal for service-based businesses and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies, they’re less suited for e-commerce businesses selling physical products. For e-commerce businesses, Google Shopping Ads are often a better option.
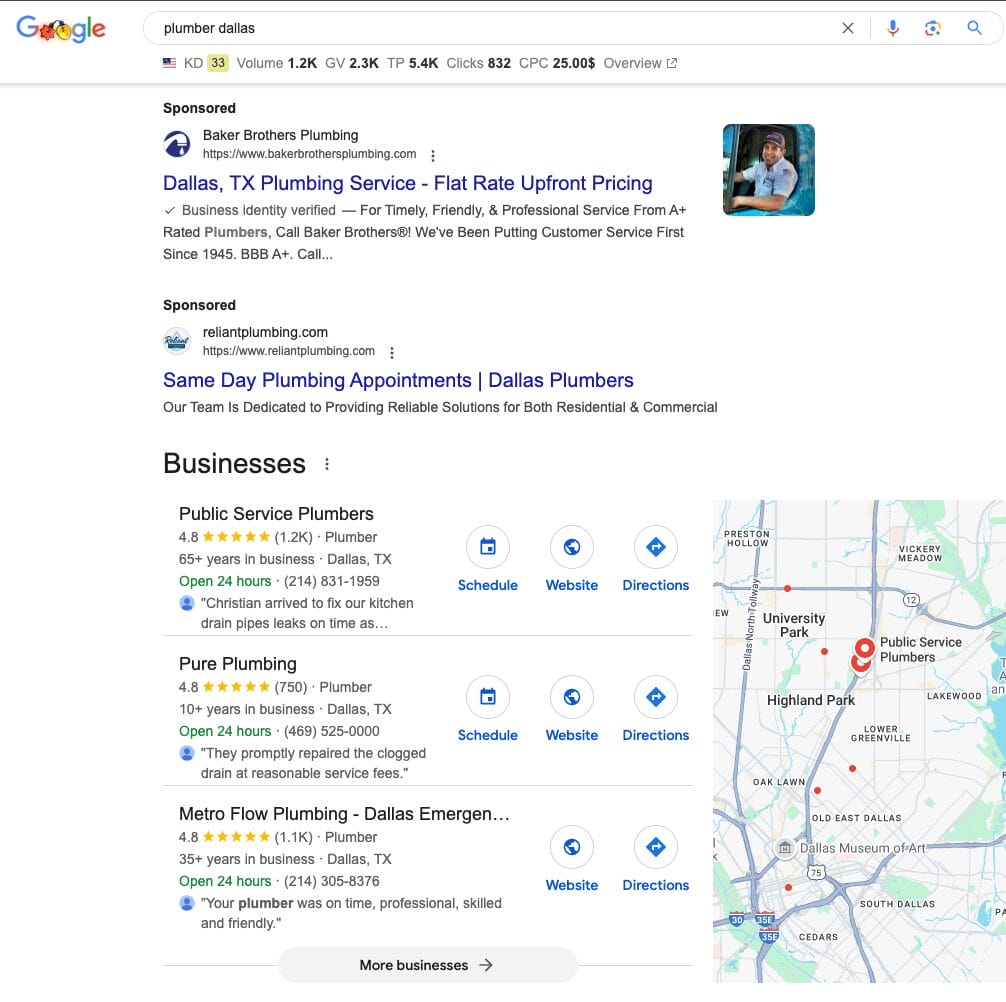
The main difference is that Google Search Ads appear as text-based ads at the top or bottom of search results (screenshot above).
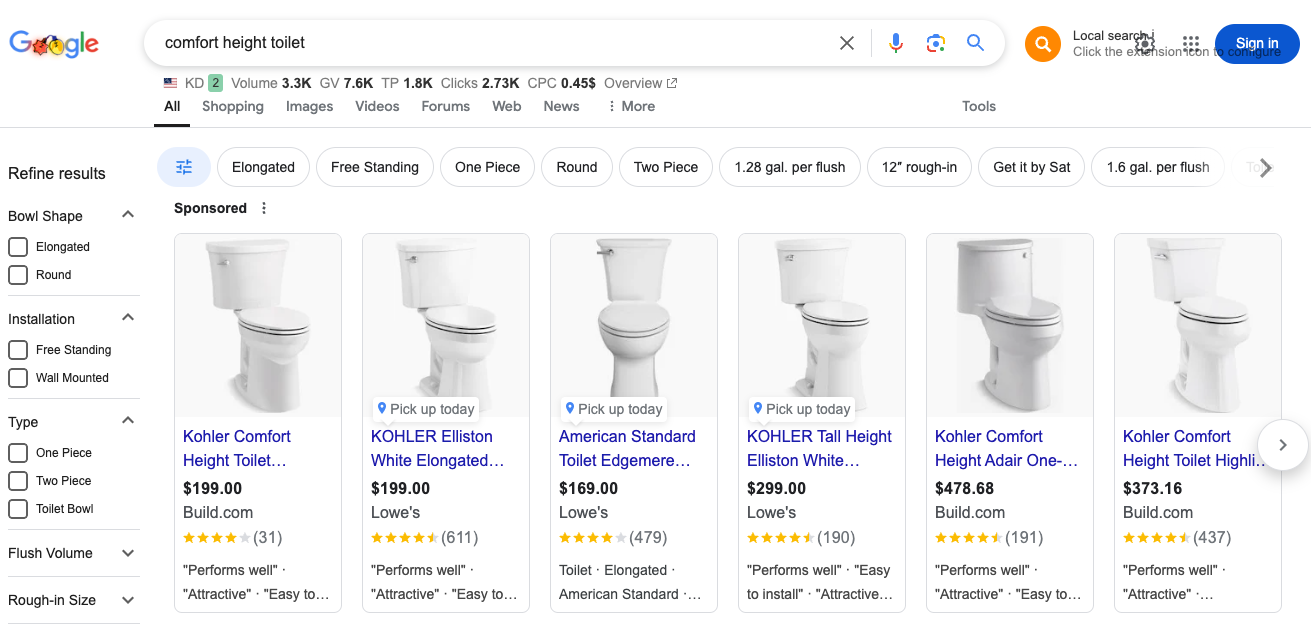
Google Shopping Ads display product images and prices in a visual grid format (screenshot below), making them more effective for showcasing physical products.
Let’s examine how Google Search Ads work and understand why they drive small business growth and create opportunities for expansion.
Why Google Search Ads
Search ads are unique because they target users actively searching for your services. For instance, when someone looks up “roof repair near me,” a roofing company’s ad can appear at the top, offering a direct solution to their need.
To reinforce that, Google Search Ads are effective because:
- You reach people actively searching for what you offer, making them more likely to convert.
- Ads run on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, so you only pay when someone clicks your ad.
- Google Search had a market of 89.73% in 2024, so nine out of ten people who are searching are using Google.
Google Ads’ default settings often prioritize spending rather than results. Without proper setup, campaign strategy, and management, you risk quickly exhausting your budget with minimal returns.
How Google Search Ads Work
Google Search Ads operates on a keyword-based auction system. This means you bid on specific search terms, like “plumbing services” or “SEO for small businesses,” that trigger your ad when users search for them.
The Basics
- Keywords: Your chosen keywords determine when your ad appears. For example, a landscaping business might target terms like “lawn care services near me” or “tree trimming experts.”
- Bidding: You set a maximum bid or use goal-based bidding, which focuses on maximizing your bids for conversion or clicks. Importantly, though, your bid isn’t the only factor determining whether your ad appears.
- Ad Rank: Google ranks ads based on their relevance, click-through rate (CTR), and the quality of your landing page. A well-crafted strategy with a closely aligned campaign and landing page can outrank competitors with higher bids. This point can’t be underscored enough: You can’t run a campaign for lawn mowing Austin unless you have a lawn mowing business in Austin with a closely related lawn mowing page.
Ad rank is combined with a few other factors, like landing page experience and keyword quality score. This complex calculation ensures Google shows ads that are most useful to users while helping businesses compete effectively, regardless of budget size.
Why Expert Management Is Crucial
Google Ads’ default settings are optimized to generate the highest number of clicks, but this does not always ensure optimal results.
For instance, without adjustments, your ads might:
- Ads may reach individuals outside your service area, reducing their effectiveness.
- Broad keyword matches cause your ads to display alongside unrelated or even competitor searches. For example, if someone searches for a competitor by name, it’s unlikely they’ll switch to your business, so spending money on these clicks is inefficient.
- Generic queries like “clogged toilet youtube” can quickly eat up your budget, but won’t bring in new customers. Those very specific searches are from users seeking DIY help, so allocating your budget when they’re ready to hire a pro is a better investment.
An experienced Google Ads agency can ensure your campaigns are set up and optimized for results, not just clicks. Here’s how:
- Targeting the Right Audience: Adjust settings to focus on specific geographic areas, devices, and demographics. For example, a local accounting firm might target ads only to users within a 20-mile radius.
- Optimizing Keywords: Use phrase or exact match to avoid irrelevant clicks and spend. Broad match often wastes budget.
- Improving Ad Quality: Craft compelling, relevant ad copy and ensure your landing pages deliver what the ad promises.
Why Strategy Matters
Let’s say a local pest control business launches a Google Ads campaign with the keyword pest control. Without proper setup, their ad might trigger searches like “DIY pest control” or “best home pesticides,” which won’t lead to sales.
By refining its strategy, the business could focus on high-intent keywords like “emergency pest control near me,” “urgent pest infestation,” or “pest control service.” These keywords are more likely to be used by customers ready to take action, ensuring the ad links to a landing page with clear contact information and a compelling offer.
This targeting leads to better-quality leads, a higher return on investment, and a lower cost-per-conversion, a metric measuring how much each lead costs your business.
Why Landing Pages Are Key
A great ad can grab attention, but conversions happen on the landing page. Users should find what they want when they click on your ad.
What Makes a Good Landing Page?
- Clear Messaging: Match the headline with the ad’s promise. If your ad offers “free consultations,” make that prominent on the landing page.
- Fast Loading: Pages should load quickly on all devices, especially mobile. Slow pages lead to lost customers.
- Strong Calls-to-Action (CTA): Guide users toward the next step, like booking a consultation or filling out a contact form.
For example, a law firm’s “free case evaluations” ad should link to a landing page with a form to schedule a consultation—not a generic homepage.
The Importance of Diversifying Your Marketing
Google Search Ads are a powerful tool, but no single marketing channel should carry your entire strategy. Changes to Google’s algorithms, costs, or policies could impact your campaigns.
To avoid putting all your eggs in one basket, consider diversifying with:
- Google Shopping Ads for e-commerce businesses.
- Organic SEO to build long-term visibility.
- Social Media Ads to engage broader audiences.
- Email Marketing to nurture leads and retain customers.
A diversified approach ensures your business remains resilient, even as platforms and trends evolve.
Google Search Ads Work
Google Search Ads are an excellent fit for service-based businesses and SaaS companies looking to reach high-intent customers. With the right keywords, compelling ad copy, and optimized landing pages, you can drive traffic, generate leads, and grow your business.
If you’re ready to harness the power of Google Search Ads, Garrett Digital can help. Contact us today to get started!